3 min
Low-code – the future of software development?
Today’s business is forced to quickly test and deploy ever-newer IT systems to run smoothly in an increasingly dynamic environment. Their primary task is to facilitate the work that managers do, but also their employees.
Here comes a long-running problem with the organization’s programming resources and the costs of subsequent projects that consume a large part of the budget. The answer may be low-code development platforms (LCDP). Today, these platforms are primarily used to design and implement user interfaces, design business processes, and their automation.
Low-code – what it actually is?

The term low-code was invented by Forrester company. In the “New Development Platforms Emerge For Customer-Facing Applications” report, they describe low-code solutions as platforms that enable business applications to be delivered quickly with minimal hand-coding and minimal initial set-up, training and implementation.
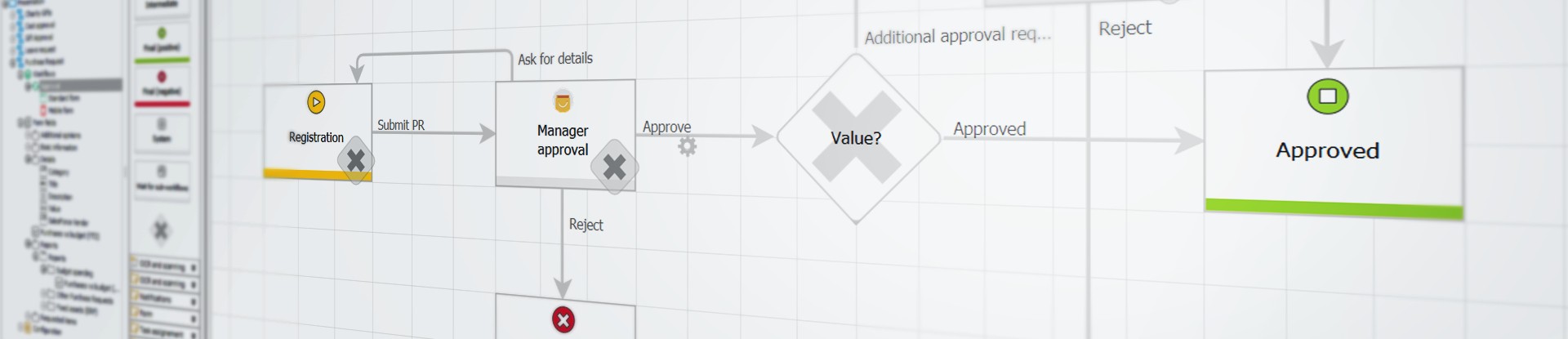
When we talk about low-code platforms, we mostly think about a visual approach to creating an application. When we build a solution, we use drag-and-drop or point-and-click mechanisms from the graphical interface. This does not mean that we do without programming knowledge, because basic skills are required from the user.
Low-code makes building, modifying and maintaining new applications easy and what is important, it saves a lot of time and the results of our work are visible immediately.
Low-code – what are the advantages?
Low-code platforms eliminate the gap between business needs and the software that is provided. They offer a wide range of tools and capabilities that vary to meet the specific needs of professional programmers and business users. Programmers want to develop creative solutions to complex problems.
The low-code platform provides developers with dedicated Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to extend an application with custom code, it enables to use data from multiple sources, create mobile applications quickly, or use a micro-service architecture. Front-end, back-end, web and mobile developers can create applications for multiple environments from start to finish. Gartner found that 66% of low-code users are professional IT developers in given organization.
In addition, the platform allows business users to build basic applications that increase the
productivity, and IT department still has insights into the application environment of their organization. The best example of using these tools is ability to create MVP projects to test new business ideas on stable prototypes and get quick feedback.
We should remember that low-code will not replace traditional programming methods any time soon. However, it is worth noting that many of the current processes that are crucial to your business can be built on low-code platforms.
Low-code – what makes it special?
There are several features associated with low-code platforms that distinguish them from other systems.
• Speed
Code creation has been reduced to a minimum, we use pre-made parts that do not in any way limit us in building complex and functional solutions. We will not only save time, but also minimize the costs associated with developing applications. With low-code platforms, we can easily make changes in running solutions in a production environment. Updates are available for all business users as they have been modified.
• Agility
With low-code platforms, we are able to create applications with an iterative method, that is improve gradually, change and modify product elements or multiple products at once, so that you can work and focus on the overall image of creating system.
• Involvement
Subsequent releases of the application allow business users to quickly learn about new functionality. This allows us to consult and implement changes to the solution on an ongoing basis. The reduced time of subsequent releases and the smooth implementation of modifications, gives business users a feeling of influence on the final design and scope of the implemented solution.
In summary, even though the most of low-code platforms users areprofessional IT developers, more than 30% are business users that are named citizen developers (a non-professional developer who creates applications for use by others in the organization that he works in). More and more companies are using low-code platforms to enable citizen developers to streamline internal processes while offloading IT. This allows highly qualified developers to focus on complex elements in digital transformation projects (integrations, dedicated modules, etc.).
Companies realized the advantages of low-code platforms during the COVID-19 crisis. It has become a stable tool, that they use to work more effectively, in and out of the office.

